Mac Optimization Mac software To access office work or essential files remotely when working from home, we all use the remote control desktop sharing apps. One most popular amongst them is TeamViewer.
After installing TeamViewer and first connection to the network, the program receives a unique identification number (ID). It allows remote users to perform a remote connection to your computer and vice versa. If you are using a free version of TeamViewer to connect to different computers (commercial purposes), here is a high probability that your remote connections will be limited on the TeamViewer server to a value not exceeding five minutes, after which the connection will be terminated.
A: Syncro Live and its suite of tools will not be supported in our Mac Agent v2. Currently, our TeamViewer and ScreenConnect integrations are supported and we have planned improvements to our remote access functionality which will may be included as part of the Mac Agent v2 sometime in the future. Q: Is Syncro Backups supported? The TeamViewer remote connectivity cloud platform enables secure remote access to any device, across platforms, from anywhere, anytime. TeamViewer connects computers, smartphones, servers, IoT devices, robots — anything — with fast, high performance connections through our global access network even in outer space or low bandwidth environments. Now if you don’t see TeamViewer in the list then click plus icon and from Application folder Select latest TeamViewer. Then tick the TeamViewer and TeamViewDesktop to allow TeamViewer to access the disk. Ii) Full Disk Access: In Full Disk Access make sure TeamViewer is ticked just like Accessibility.
In the left pane, select Full Disk Access. If you see TeamViewer in the list, check the box next to it: If you don't see TeamViewer in the list, click the + icon. Navigate to Applications TeamViewer. The following message appears: “TeamViewer” will not have full disk access until it is quit. Restart your computer. Starting with macOS 10.14, Mojave; Intego software may require Full Disk Access to scan your Mail, Messages, Safari files, and other user data. Full Disk Access is a new security feature in macOS Mojave that requires some applications to be given full permission to access a user's protected files.
If the TeamViewer servers decide that you are using the utility for commercial purposes to connect to multiple customer computers, a warning window may appear:
Show All Repair Parts for LF Power Inverter. Generator; Batteries; User Manual of LF Power Inverters; Helen; Jack. 5000w LF Pure power inverter, DC12V to AC110v/60Hz or 220v/50Hz or 220v/60Hz UPS, US $ 400 - 450 / Carton, China, POWER JACK, LFPSW-5000-12/110 or 220.Source from POWER JACK'S ELECTRIC CO., LTD. Power jack lfpsw-5000 user manual. Screw Jacks Back to Top. Maintenance manual for C-Series metric machine screw jacks - cubic gearbox design. C-Series Quick Guide Manual(EN. 3000W LF PSW Power Inverter DC 12V to AC 110V1.Ideally suitable for Journeys, Camping, Tents, Boat T.
Your trial period has expired
The commercial usage message in TeamViewer v14 looks as follows:
Commercial use detected
This software seems to be used in commercial environments. Please note that the free version may only be used for personal use.
Your session will be terminated after 5 minutes.

The trial version TeamViewer expiration message usually appears after a couple of days of use.
In this case, you can try to reinstall TeamViewer, but that won’t help you. The only way to unblock the limitation is to reset TeamViewer ID (or purchase a license ).
You can see your TeamViewer ID on the main screen when running the application.
TeamViewer Versions: Trial Expiration Problem
There are two TeamViewer versions:
- Free version (non-commercial use) — designed for home use and connecting to a small number of PCs;
- Paid (commercial) version — the number of connected PCs and the duration of the sessions are unlimited.
If you use TeamViewer for personal use only, here’s how to fix the TeamViewer trial expired problem.
Make sure that you and the users you are connecting using the free version of TeamViewer. If one user uses a free one and the second uses a commercial one, then the commercial version will consider the use of TeamViewer in the commercial purpose.
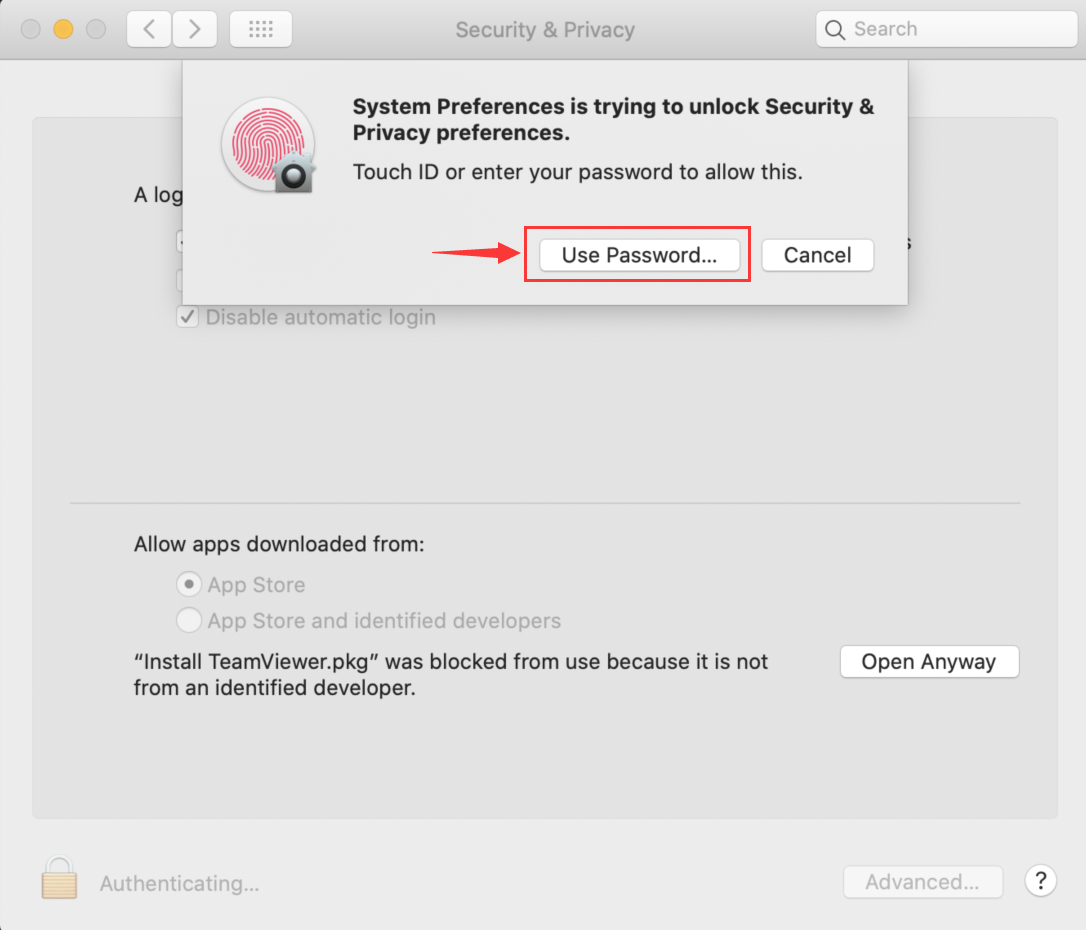
If the commercial version of TeamViewer is installed, you need to remove it, clear the registry and folders from the remaining entries and files, and install the free version of TeamViewer.
- Go to Add or remove programs, find TeamViewer in the list and select Uninstall;
- After removing the program, press Win+R > %Appdata% 0 > OK. Remove the folder TeamViewer;
- Then delete the directory C:Program FilesTeamViewer;
- Delete the following registry key using the Registry Editor (regedit.exe): ComputerHKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareTeamViewer and ComputerHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREWOW6432NodeTeamViewer
- Reboot your computer;
- Download and install the TeamViewer free edition (press “Download for free” on TW site);
If this does not work, move on. There is another more difficult way to extend the TeamViewer usage by resetting TeamViewer ID.
TeamViewer ID is generated based on several unique attributes of your computer:
- MAC address of the network card;
- VolumeID of disk partition;
- Creation date of folder Program Files.
Accordingly, to change TeamViewer ID, you need to change these 3 values.
Reset or Change TeamViewer ID in Windows
To reset the TeamViewer ID, you need to perform a few steps.
First of all, kill the TeamViewer.exe process. Then you need to remove the current TeamViewer ID from the registry.
- In Windows x86, TeamViewer version [X], open regedit.exe, go to the registry key HKLMSOFTWARETeamViewerVersion[X] and delete DWORD value ClientID;
- In Windows x64, delete value ClientID from HKLMSOFTWAREWow6432NodeTeamViewerVersion[X];
- Check if the registry key HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareTeamViewer exists and delete it.
To change the creation date of Program Files folder, you can use the NirCMD utility. Download it and run the following command in the elevated Command prompt console:
To change the MAC address of the network card, you can use special utilities or use the following instructions for manually edit MAC address in the registry.
To get the current MAC address of your network card, open Command prompt and run the following command:
We are interested in two parameters:
- Description (LAN card description) – Intel(R) 82574L Gigabit Network Connection
- Physical Address (MAC address) – 00-50-56-9E-FC-CB
Then, open Registry Editor and go to the key HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlClass{4d36e972-e325-11ce-bfc1-08002be10318}.
Each network component in this branch is indicated by four digits starting from 0000, 0001 and so on. You can find the right key by browsing it and looking for DriverDesc option, where the description (name) of your NIC must be specified, for example, Intel(R) 82574L Gigabit Network Connection.
Once the correct network card is found, add or modify REG_SZ parameter named NetworkAddress, which defines MAC (hardware) address of the network card. It is enough to change a single digit in the current MAC address, for example, 0050560EFCCB.
So, the MAC address of the network card is changed. Now you need to change VolumeID of the system partition. VolumeID (or Volume Serial Number) is a unique identifier of a volume on a hard drive, which is set during formatting.
Note. In some cases, TeamViewer is linked to a non-system volume of the disk, or even to the removable media volume, so it is likely that we need to change VolumeID of other partitions.
To change VolumeID use the console utility VolumeID v2.1. Download and extract archive VolumeId.zip.
Check the current VolumeID by opening a command prompt with Administrator privileges and execute the command:
Volume Serial Number is 5E37-ECE1.
Change current value to new value 5E37-EC11:
OnceVolumeId utility updated the volume serial number of your system partition, close the Command Prompt window, and reboot your computer.
After rebooting, run the app and you will be assigned a new TeamViewer ID.
How to Reset TeamViewer ID on Linux?
In case you are using TeamViewer on one of the Linux distributions, you can follow the instructions below to reset the TeamViewer ID. The method is tested on Debian 9 and with some modifications you can use it on any Linux distribution.
- Uninstall Teamviewer with su privileges;
- Remove the file /var/lib/dbus/machine-id if exist;
- Edit the GUID (you can just replace the last character): mc -e id.txt;
- Change the MAC address of the network card:
- Correct string:
pre-up ifconfig eth0 hw ether New_MAC_HERE - Reboot OS;
- Install Teamviewer, it should get a new ClientID.
In the Linux Mint distro, you can reset TeamViewer ID as follows:
- Delete TeamViewer:sudo dpkg -r teamviewer
- Remove the binding file (if exists): sudo rm /var/lib/dbus/machine-id
- Change the NIC’s MAC address;
- Install the TeamViewer package again: sudo dpkg -i teamviewer_13.2.13582_amd64.deb
- If an error with the missing packages occurs, run the command: sudo apt-get install -f
To change ClientID on a cloned Linux machine it’s enough to:
- Stop the TeamViewer daemon;
- Delete TeamViewer settings:
- Remove folder /opt/teamviewer{TW_VERSION_Here)/config;
- Start the TeamViewer daemon.
How to Change TeamViewer ID on Mac OS?
To change TeamViewer ClientID on the Mac OS, you can use the python script TeamViewer-id-changer.py from GitHub. Follow these steps
- Download script from Git Hub;
- Close TeamViewer (make sure the TeamViewer process has completely disappeared from the process list);
- Run the script: sudo ./TeamViewer-id-changer.py;
- Reboot the device.
This script works correctly for TeamViewer 11, 12, 13 (not tested in TeamViewer 14).
If reinstalling and resetting TeamViewer ClientID did not help you, and you are sure that you are using TeamViewer for personal use only, you can create a ticket request using the online form to unlock your device (https://www.teamviewer.com/en/support/commercial-use-suspected/). Fill the form, specify a specific TeamViewer ID from your device and send a request.
Teamviewer Mac Access
After a while (3-5 days), TeamViewer support will answer on your request: your device will be unlocked or your “commercial use” label will remain for your ID. If you use TeamViewer for commercial purposes, buy a license, or try another free remote product to manage your users and customers.
The post How to Reset TeamViewer ID? appeared first on TheITBros.
Skip to end of metadataGo to start of metadataTeamViewer installation for Mac to access remotely a work computer from home.
Step-by-step guide
- Download TeamViewer and install it
- Download website (also available on Canvas on Texas Undergraduate Studies course for UGS staff):
https://www.teamviewer.com/en-us/ - Download through 'Download for free' option.
- Start installation process, agree to the terms and conditions when prompted.
Provide User Name and Password, and click on Install.
- Download website (also available on Canvas on Texas Undergraduate Studies course for UGS staff):
- Initial Setup
- TeamViewer should automatically start up with an ‘Initial Setup’ pop-up window. Click ‘Continue’.
You can set your personal password. This password is needed to remotely access your computer from another device with a TeamViewer client. If you don’t need remote access to your machine, you can skip this step. It is possible to set the password later on TeamViewer preferences if needed. Click ‘Continue’ or ‘Skip’.
Note
If you are installing TeamViewer in your personal computer to remotely access your work computer, it might not be absolutely necessary to set up a password in your personal computer. However, if you are configuring your work computer’s password, make sure to contact your IT Coordinator first.
Click on ‘Finish’, the TeamViewer client should open up.
- TeamViewer should automatically start up with an ‘Initial Setup’ pop-up window. Click ‘Continue’.
- Authorize system access to TeamViewer
- A yellow warning sign should initially appear on the upper left corner labeled as “Check System Access”, click on it.
- A pop-up window should appear. We need to provide permissions to TeamViewer to access all system capabilities necessary for it to function properly. First, let’s grant it Screen Recording access. Click on “Open Screen Recording Preferences”.
- In the new Security and Privacy window click on the lock in the lower left corner to be able to make changes, and provide your User Name and Password.
A TeamViewer Icon should be visible in the list of programs. Click on its checkbox.
- A small pop-up window should appear asking to quit “TeamViewer” for it to be able to have screen recording capabilities. Click on ‘later’, we’ll quit TeamViewer and restart it at the end of the set up.
- Go back to the ‘Review System Access’ window in TeamViewer. ‘Screen Recording’ should now appear as ‘Allowed’. Click now on ‘Request Access…’ under ‘Accessibility. Proceed to click on “Open System Preferences” in the pop-up window.
- In the Security and Privacy window, the make changes lock should be unlocked already, however, if not, proceed to unlock it again by clicking on it and providing credentials. In the list of programs being shown, enable the checkbox of TeamViewer.
- Go back to the ‘Review System Access’ window in TeamViewer. ‘Accessibility’ should now appear as ‘Allowed’ as well. Click now on ‘Open Full Disk Access Preferences…’ under ‘Full Disk Access’.
- On the Security and Privacy window, make sure again the lock in the lower left corner is open. TeamViewer might not be visible in this case among the list of programs. To add TeamViewer to the list of programs being shown, click on the plus sign ‘+’ at the bottom of the list.
- A Finder window should appear, go into Applications and look for the TeamViewer Icon. Select the TeamViewer icon and click ‘Open’
- TeamViewer should now be among the list of programs. Its checkbox will be automatically enabled, if not, enable it.
- A small pop-up window will prompt you again to quit TeamViewer. Click on ‘Quit Now’. TeamViewer should automatically close.
- Open TeamViewer again. Verify the yellow warning sign has disappeared now.
- A yellow warning sign should initially appear on the upper left corner labeled as “Check System Access”, click on it.
- FOR WORK COMPUTER ONLY: Configure ‘Prevent computer from sleeping automatically’
If TeamViewer is being installed/configured in a work computer (the one that will be remotely accessed from a personal/home computer), it is necessary to prevent the computer from going into sleep mode, otherwise, the computer would not be available for remote access from home.- Go into System Preferences, and click on ‘Energy Saver’
- Unlock the ‘make changes’ lock on the lower left corner by providing your User Name and Password.
- Enable “Prevent computer from sleeping automatically when display is off”, and lock the ‘make changes’ lock.
- Go into System Preferences, and click on ‘Energy Saver’
Teamviewer Helper Tool Mac Shortcut
Related articles
-->This article describes the settings you can control and restrict on macOS devices. As part of your mobile device management (MDM) solution, use these settings to allow or disable features, set password rules, allow or restrict specific apps, and more.
These settings are added to a device configuration profile in Intune, and then assigned or deployed to your macOS devices.
Note
The user interface may not match the enrollment types in this article. The information in this article is correct. The user interface is being updated in an upcoming release.
Before you begin
Create a macOS device restrictions configuration profile.
Note
These settings apply to different enrollment types. For more information on the different enrollment types, see macOS enrollment.
Built-in Apps
Settings apply to: All enrollment types
Block Safari AutoFill: Yes disables the autofill feature in Safari on devices. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow users to change autocomplete settings in the web browser.
Block use of camera: Yes prevents access to the camera on devices. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow access to the device camera.
Intune only manages access to the device camera. It doesn't have access to pictures or videos.
Block Apple Music: Yes reverts the Music app to classic mode, and disables the Music service. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow using the Apple Music app.
Block spotlight suggestions: Yes stops Spotlight from returning any results from an Internet search. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow Spotlight search to connect to the Internet, and get search results.
Block file transfer using Finder or iTunes: Yes disables application file sharing services. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow application file sharing services.
This feature applies to:
- macOS 10.13 and newer
Cloud and storage
Settings apply to: All enrollment types
Block iCloud Keychain sync: Yes disables syncing credentials stored in the Keychain to iCloud. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow users to sync these credentials.
Block iCloud Desktop and Document Sync: Yes prevents iCloud from syncing documents and data. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow document and key-value synchronization to your iCloud storage space.
Block iCloud Mail Backup: Yes prevents iCloud from syncing to the macOS Mail app. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow Mail synchronization to iCloud.
Block iCloud Contact Backup: Yes prevents iCloud from syncing the device contacts. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow contact sync using iCloud.
Block iCloud Calendar Backup: Yes prevents iCloud from syncing to the macOS Calendar app. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow Calendar synchronization to iCloud.
Block iCloud Reminder Backup: Yes prevents iCloud from syncing to the macOS Reminders app. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow Reminders synchronization to iCloud.
Block iCloud Bookmark Backup: Yes prevents iCloud from syncing the device Bookmarks. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow Bookmark synchronization to iCloud.
Block iCloud Notes Backup: Yes prevents iCloud from syncing the device Notes. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow Notes synchronization to iCloud.
Block iCloud Photos backup: Yes disables iCloud Photo Library, and prevents iCloud from syncing the device photos. Any photos not fully downloaded from iCloud Photo Library are removed from local storage on devices. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow syncing photos between the device and the iCloud Photo Library.
Block Handoff: This feature allows users to start work on a macOS device, and then continue the work they started on another iOS/iPadOS or macOS device. Yes prevents the Handoff feature on devices. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow this feature on devices.
This feature applies to:
- macOS 10.15 and newer
Connected devices
Settings apply to: All enrollment types
- Block AirDrop: Yes prevents using AirDrop on devices. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow using the AirDrop feature to exchange content with nearby devices.
- Block Apple Watch auto unlock: Yes prevents users from unlocking their macOS device with their Apple Watch. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow users to unlock their macOS device with their Apple Watch.
Domains
Settings apply to: All enrollment types
- Unmarked Email Domains: Enter one or more Email domain URLs to the list. When users send or receive an email from a domain other than the domains you added, the email is marked as untrusted in the macOS Mail app.
General
Settings apply to: All enrollment types
Block Lookup: Yes prevents user from highlighting a word, and then looking up its definition on the device. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow the definition lookup feature.
Block dictation: Yes stops users from using voice input to enter text. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow users to use dictation input.
Block content caching: Yes prevents content caching. Content caching stores app data, web browser data, downloads, and more locally on devices. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might enable content caching.
For more information on content caching on macOS, see Manage content caching on Mac (opens another website).
This feature applies to:
- macOS 10.13 and newer
Block screenshots and screen recording: Device must be enrolled in Apple's Automated Device Enrollment (DEP). Yes prevents users from saving screenshots of the display. It also prevents the Classroom app from observing remote screens. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow users to capture screenshots, and allows the Classroom app to view remote screens.
Settings apply to: User approved device enrollment, Automated device enrollment (supervised)
Defer software updates: Yes allows you to delay when OS updates and non-OS updates are shown on devices. This setting doesn't control when updates are or aren't installed. When nothing is selected, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
By default, the OS might show updates on devices as Apple releases them. By default, software updates aren't delayed. If you configure this setting, then OS and non-OS software updates are delayed, depending on the options you select. The drop-down does exactly what you choose. It can delay both, delay neither, or delay one of them.
For example, if a macOS update gets released by Apple on a specific date, then that update naturally shows on devices around the release date. Seed build updates are allowed without delay.
Delay visibility of software updates: Enter a value from 0-90 days. By default, updates are delayed for
30days. This value applies to the Defer software updates options you select. If you only select Operating system updates, then only OS updates are delayed for 30 days. If you select Operating system updates and Non operating system updates, then both are delayed for 30 days.When the delay expires, users get a notification to update to the earliest version available when the delay was triggered.
For example, if a macOS update is available on January 1, and Delay visibility is set to 5 days, then the update isn't shown as an available update. On the sixth day following the release, that update is available, and users can install it.
This feature applies to:
- macOS 10.13.4 and newer
Settings apply to: Automated device enrollment
Disable AirPlay, view screen by Classroom app, and screen sharing: Yes blocks AirPlay, and prevents screen sharing to other devices. It also prevents teachers from using the Classroom app to see their students' screens. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow teachers to see their students' screens.
To use this setting, set the Block screenshots and screen recording setting to Not configured (screenshots are allowed).
Allow Classroom app to perform AirPlay and view screen without prompting: Yes lets teachers see their students' screens without requiring students to agree. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might require students to agree before teachers can see the screens.
To use this setting, set the Block screenshots and screen recording setting to Not configured (screenshots are allowed).
Require teacher permission to leave Classroom app unmanaged classes: Yes forces students enrolled in an unmanaged Classroom course to get teacher approval to leave the course. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow students to leave the course whenever the student chooses.
Allow Classroom to lock the device without prompting: Yes lets teachers lock a student's device or app without the student's approval. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might require students agree before teachers can lock the device or app.
Students can automatically join Classroom class without prompting: Yes lets students join a class without prompting the teacher. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might require teacher approval to join a class.
Password
These settings use the Passcode payload (opens Apple's web site).
Important
On macOS devices running 10.14.2 to 11.x (except all versions of macOS 10.15 Catalina), users are prompted to change the device password when the device updates to a new major OS version. This password update happens once. After users update the password, any other password policies are enforced. If a passcode is required in at least one policy, then this behavior only occurs for the local machine user.
Any time the password policy is updated, all users running these macOS versions must change the password, even if the current password is compliant with the new requirements. For example, when your macOS device turns on after upgrading to Big Sur (macOS 11), users need to change the device password before they can sign in.
Settings apply to: All enrollment types
Require password: Yes requires users to enter a password to access devices. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might not require a password. It also doesn't force any restrictions, such as blocking simple passwords or setting a minimum length.
Required password type: Enter the required password complexity level your organization requires. When left blank, Intune doesn't change or update this setting. Your options:
- Not configured: Uses the device default.
- Alphanumeric: Includes uppercase letters, lowercase letters, and numeric characters.
- Numeric: Password must only be numbers, such as 123456789.
This feature applies to:
- macOS 10.10.3 and newer
Number of non-alphanumeric characters in password: Enter the number of complex characters required in the password, from 0-4. A complex character is a symbol, such as
?. When left blank or set to Not configured, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.Minimum password length: Enter the minimum length the password must have, from 4-16 characters. When left blank, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
Block simple passwords: Yes prevents using simple passwords, such as
0000or1234. When the value is blank or set to Not configured, Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow simple passwords.Maximum minutes of inactivity until screen locks: Enter the length of time devices must be idle before the screen is automatically locked. For example, enter
5to lock devices after 5 minutes of being idle. When the value is blank or set to Not configured, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.Maximum minutes after screen lock before password is required: Enter the length of time devices must be inactive before a password is required to unlock it. When the value is blank or set to Not configured, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
Password expiration (days): Enter the number of days until the device password must be changed, from 1-65535. For example, enter
90to expire the password after 90 days. When the password expires, users are prompted to create a new password. When the value is blank or set to Not configured, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.Prevent reuse of previous passwords: Restrict users from creating previously used passwords. Enter the number of previously used passwords that can't be used, from 1-24. For example, enter 5 so users can't set a new password to their current password or any of their previous four passwords. When the value is blank, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
Maximum allowed sign-in attempts: Enter the maximum number of times that users can consecutively try to sign in before the device locks users out, from 2-11. When this number is exceeded, the device is locked. We recommend not setting this value to a low number, such as
2or3. It's common for users to enter the wrong password. We recommend setting to a higher value.For example, enter
5so users can enter the wrong password up to five times. After the fifth attempt, the device is locked. If you leave this value blank, or don't change it, then11is used by default.After six failed attempts, macOS automatically forces a time delay before a passcode can be entered again. The delay increases with each attempt. Set the Lockout duration to add a delay before the next passcode can be entered.
Lockout duration: Enter the number of minutes a lockout lasts, from 0-10000. During a device lockout, the sign in screen is inactive, and users can't sign in. When the lockout ends, user can try to sign in again.
If you leave this value blank, or don't change it, then
30minutes is used by default.This setting applies to:
- macOS 10.10 and newer
Block user from modifying passcode: Yes stops the passcode from being changed, added, or removed. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow passcodes to be added, changed, or removed.
Block Touch ID to unlock device: Yes prevents using fingerprints to unlock devices. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow users to unlock the device using a fingerprint.
Block password AutoFill: Yes prevents using the AutoFill Passwords feature on macOS. Choosing Yes also has the following impact:
- Users aren't prompted to use a saved password in Safari or in any apps.
- Automatic Strong Passwords are disabled, and strong passwords aren't suggested to users.
When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow these features.
Block password proximity requests: Yes prevents devices from requesting passwords from nearby devices. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow these password requests.
Block password sharing: Yes prevents sharing passwords between devices using AirDrop. When set to Not configured (default), Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, the OS might allow passwords to be shared.
Teamviewer Allow Access On Mac
Privacy preferences
On macOS devices, apps and processes often prompt users to allow or deny access to device features, such as the camera, microphone, calendar, Documents folder, and more. These settings allow administrators to pre-approve or pre-deny access to these device features. When you configure these settings, you manage data access consent on behalf of your users. Your settings override their previous decisions.
The goal of these settings is to reduce the number of prompts by apps and processes.
This feature applies to:
- macOS 10.14 and newer
- Some settings apply to macOS 10.15 and newer.
- These settings only apply on devices that have the privacy preferences profile installed before being upgraded.
Settings apply to: User approved device enrollment, Automated device enrollment
- Apps and processes: Add apps or processes to configure access. Also enter:
Name: Enter a name for your app or process. For example, enter
Microsoft Remote DesktoporMicrosoft 365.Identifier type: Your options:
- Bundle ID: Select this option for apps.
- Path: Select this option for non-bundled binaries, which is a process or executable.
Helper tools embedded within an application bundle automatically inherit the permissions of their enclosing application bundle.
Identifier: Enter the app bundle ID, or the installation file path of the process or executable. For example, enter
com.contoso.appname.To get the app bundle ID, open the Terminal app, and run the
codesigncommand. This command identifies the code signature. So you can get the bundle ID and the code signature simultaneously.Code requirement: Enter the code signature for the application or process.
A code signature is created when an app or binary is signed by a developer certificate. To find the designation, run the
codesigncommand manually in the Terminal app:codesign --display -r - /path/to/app/binary. The code signature is everything that appears after=>.Enable static code validation: Choose Yes for the app or process to statically validate the code requirement. When set to Not configured, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
Enable this setting only if the process invalidates its dynamic code signature. Otherwise, use Not configured.
Block Camera: Yes prevents the app from accessing the system camera. You can't allow access to the camera. When set to Not configured, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
Block Microphone: Yes prevents the app from accessing the system microphone. You can't allow access to the microphone. When set to Not configured, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
Block screen recording: Yes blocks the app from capturing the contents of the system display. You can't allow access to screen recording and screen capture. When set to Not configured, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
Requires macOS 10.15 and newer.
Block input monitoring: Yes blocks the app from using CoreGraphics and HID APIs to listen to CGEvents and HID events from all processes. Yes also denies apps and processes from listening to and collecting data from input devices, such as a mouse, keyboard, or trackpad. You can't allow access to the CoreGraphics and HID APIs.
When set to Not configured, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
Requires macOS 10.15 and newer.
Speech recognition: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access the system speech recognition, and allows sending speech data to Apple.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing the system speech recognition, and prevents sending speech data to Apple.
Requires macOS 10.15 and newer.
Accessibility: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access to the system Accessibility app. This app includes closed captions, hover text, and voice control.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing the system Accessibility app.
Contacts: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access contact information managed by the system Contacts app.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing this contact information.
Calendar: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access calendar information managed by the system Calendar app.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing this calendar information.
Reminders: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access reminder information managed by the system Reminders app.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing this reminder information.
Photos: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access the pictures managed by the system Photos app in
~/Pictures/.photoslibrary. - Block: Prevents the app from accessing these pictures.
Media library: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access Apple Music, music and video activity, and the media library.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing this media.
Requires macOS 10.15 and newer.
File provider presence: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access the File Provider app, and know when users are using files managed by the File Provider. A File Provider app allows other File Provider apps to access the documents and directories stored and managed by the containing app.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing the File Provider app.
Requires macOS 10.15 and newer.
Full disk access: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access all protected files, including system administration files. Apply this setting with caution.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing these protected files.
System admin files: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access some files used in system administration.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing these files.
Desktop folder: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access files in the user’s Desktop folder.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing these files.
Requires macOS 10.15 and newer.
Documents folder: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access files in the user’s Documents folder.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing these files.
Requires macOS 10.15 and newer.
Downloads folder: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access files in the user’s Downloads folder.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing these files.
Requires macOS 10.15 and newer.
Network volumes: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access files on network volumes.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing these files.
Requires macOS 10.15 and newer.
Removable volumes: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to access files on removable volumes, such as a hard disk.
- Block: Prevents the app from accessing these files.
Requires macOS 10.15 and newer.
System events: Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app to use CoreGraphics APIs to send CGEvents to the system event stream.
- Block: Prevents the app from using CoreGraphics APIs to send CGEvents to the system event stream.
Apple events: This setting allows apps to send a restricted Apple event to another app or process. Select Add to add a receiving app or process. Enter the following information of the receiving app or process:
Identifier type: Select Bundle ID if the receiving identifier is an application. Select Path if the receiving identifier is a process or executable.
Identifier: Enter the app bundle ID, or the installation path of the process receiving an Apple event.
Code requirement: Enter the code signature for the receiving application or process.
A code signature is created when an app or binary is signed by a developer certificate. To find the designation, run the
codesigncommand manually in the Terminal app:codesign --display -r -/path/to/app/binary. The code signature is everything that appears after=>.Access: Allow a macOS Apple Event to be sent to the receiving app or process. Your options:
- Not configured: Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
- Allow: Allows the app or process to send the restricted Apple event to the receiving app or process.
- Block: Prevents the app or process from sending a restricted Apple event to the receiving app or process.
Save your changes.
Restricted apps
Settings apply to: All enrollment types
Type of restricted apps list: Create a list of apps that users aren't allowed to install or use. Your options:
- Not configured (default): Intune doesn't change or update this setting. By default, users might have access to apps you assign, and built-in apps.
- Approved apps: List the apps that users are allowed to install. To stay compliant, users must not install other apps. Apps that are managed by Intune are automatically allowed, including the Company Portal app. Users aren't prevented from installing an app that isn't on the approved list. But if they do, it's reported in Intune.
- Prohibited apps: List the apps (not managed by Intune) that users aren't allowed to install and run. Users aren't prevented from installing a prohibited app. If a user installs an app from this list, it's reported in Intune.
Apps list: Add apps to your list:
App Bundle ID: Enter the bundle ID of the app. You can add built-in apps and line-of-business apps. Apple's web site has a list of built-in Apple apps.
To find the URL of an app, open the iTunes App Store, and search for the app. For example, search for
Microsoft Remote DesktoporMicrosoft Word. Select the app, and copy the URL. You can also use iTunes to find the app, and then use the Copy Link task to get the app URL.App name: Enter a user-friendly name to help you identify the bundle ID. For example, enter
Intune Company Portal app.Publisher: Enter the publisher of the app.
Import a CSV file with details about the app, including the URL. Use the
<app bundle ID>, <app name>, <app publisher>format. Or, Export to create a list of apps you added, in the same format.
Next steps
Assign the profile and monitor its status.
You can also restrict device features and settings on iOS/iPadOS devices.